DDR Termination and Reference Voltage Nets
High speed DDR memory signals are terminated using a resistor that connects to a mid-rail termination-tracking voltage supply (VTT) as shown in Figure 8. The resistor (RT) typically has a value between 30 Ω and 100 Ω and, in XJTAG terminology, is referred to as a bias-termination resistor (BIAS_TERM).
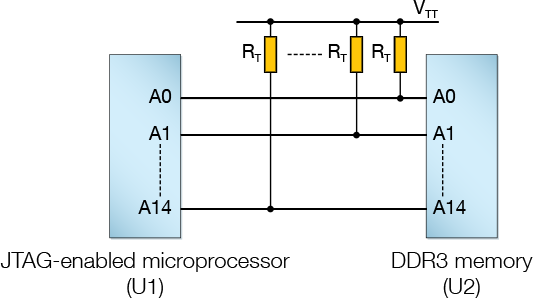
Figure 8: Termination to VTT
It is important for XJDeveloper to know which resistors are acting as terminations and which rails are termination voltages for two main reasons:
- Because VTT is a mid-rail supply, any noise on that rail could cause the values read on the device's pins to change state when the nets are undriven. To avoid this giving false errors during the connection test, the rail must be categorised as a termination voltage.
- During a boundary scan test, a large percentage of the pins connected to VTT via termination resistors can be simultaneously driven to the same level. This can sometimes be enough to cause the voltage on any undriven lines connected to VTT via the other termination resistors to shift slightly. Because the VTT supply is mid-rail, the input cells of devices pulled to it will sit close to their logic threshold, and this tiny shift in voltage can be sufficient to cause a change of state, resulting in a false indication of a short-circuit. By categorising the rail as a termination voltage and the resistors as BIAS_TERMs, the software knows to treat those lines differently.
- Note that XJDeveloper has two types of termination resistor – a bias termination (BIAS_TERM as described above) and a differential termination (DIFF_TERM), which is used for termination resistors when they are placed directly across two differential nets. A differential termination resistor is used when one device drives the two ends of the resistor to opposite values and it is therefore never connected to a fixed voltage rail.
- The difference between these types of resistor is demonstrated below, where the first application requires bias termination resistors RT connected to a fixed voltage, VTT, and the second uses a differential termination RD:
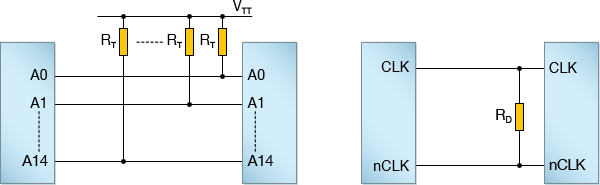
- More help on termination resistors is available from the XJTAG blog.
- Further information on the different types of resistor categorisation can be found in the XJTAG User Guide chapter on Categorising Devices.
XJTAG v4.2.3
